
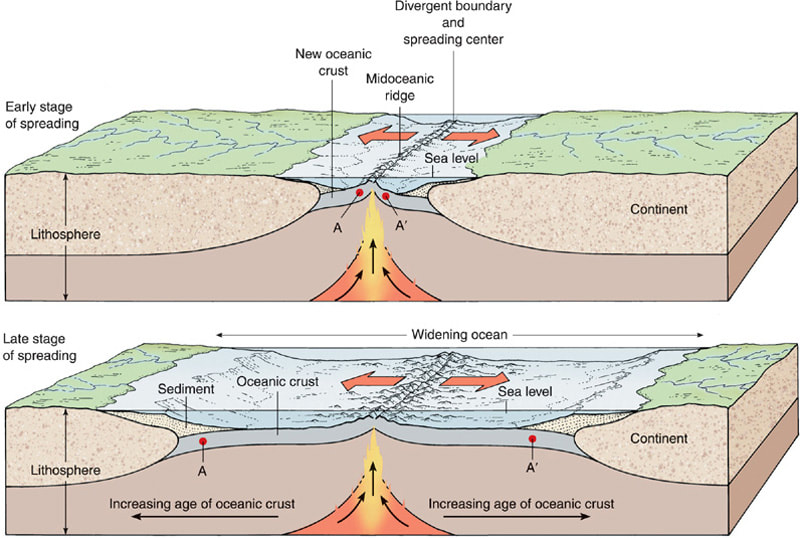
Transforms connect different plate boundaries to each other. The east coast of North America would have looked like this at about 300 Ma, prior to the assembly of Pangea.įigure 4 shows a map view of a transform boundary. The Andes mountains of South America are a modern example of the boundary illustrated in Figure 3. Ocean-ocean and continent-continent collisions are two other types of convergent boundaries. Volcanism through the overlying plate returns some of the old lithosphere to the surface, most of the rest is recycled more slowly through the MOR system. The old oceanic plate is destroyed in the subduction zone. In this case, oceanic lithosphere subducts beneath continental lithosphere. Modern examples of these two boundaries are the East African Rift (1) and the Red Sea (2).įigure 3 is an example of a convergent plate boundary. Figure 2 shows the newly-formed east coast of North America separating from the west coast of Africa, with the incipient Atlantic Ocean in between. At 200 Ma the supercontinent Pangea began to rift as in Figure 1. Oceanic lithosphere is created at the Mid-Ocean Ridge (MOR) and the addition of new material here gradually increases the separation of the continents. Eventually, as the continent separates completely, a new ocean basin is formed between the continental fragments (Figure 2). Normal faults form and volcanoes are active along the faults. Heat within the mantle causes expansion and cracking of the overlying lithosphere. The simple figures presented here were drawn to give you a basic idea of what goes on at each boundary type.įigure 1 shows a continent in the process of rifting in two (the divergent boundary is not yet fully-formed). You should review your notes and text for the complete list. The corresponding plate boundaries are called (1) Divergent boundaries, (2) Convergent boundaries, and (3) Transform boundaries.Įach of these plate boundaries is seismically active, and each boundary type has a suite of distinctive geological features that characterize it. We determined that there are only three fundamentally different ways that plates can move with respect to one another.

Finally, we related all of the various geologic features that we have studied to plate boundaries and fit our observations into the framework of Plate Tectonics. You also explored some of the physical properties of the lithospheric plates and underlying mantle: isostacy, viscosity and convection. This week we use GIS data on earthquakes and volcanoes, allowing you to map the boundaries of the Earth's tectonic plates for yourselves. Review Plate Boundaries and Associated Structures Science in the news, courtesy of USA Today.List of Geoscience Internship Opportunities.The Paleomap Project: Follow the animations link for Earth reconstructions through time.According to the world Atlas, there are nine major plates around the earth.These plates have been named after the landforms which were found on them.Therefore the names of the plates are: North American, Eurasian,African, Indo-Australian,Australian,Indian,South American and Antarctic.Geological Sciences 101 Introduction to Geological Sciences This theory was developed from the 1950's through 1970’s. Note: The continental drift theory was first proposed by Alfred Wegener. The outer layer is known as lithosphere which has a thickness of 100 km.

Tectonic Plate theory is a scientific explanation that the outer covering of the earth is divided into several plates which slide over the mantle, which is the rocky inner layer above the core. When a divergent boundary takes place beneath the lithosphere,the convection current underneath it rises,which lifts the lithosphere,creating a mid oceanic ridge. Divergent boundaries often give rise to volcanic islands. The oceanic plates and mid-oceanic ridges are the most common places for a divergent boundary to occur. Hint:Earthquakes are common in divergent boundaries and mantle is seen rising from the earth’s mantle to the surface which solidifies to create a new oceanic crust.Ĭomplete answer: Divergent boundary is a linear feature in the theory of plate tectonics that takes place between two tectonic plates when they pull away from each other.This occurs due to the rise in convection currents.When a divergent boundary occurs in the continents,it creates a rift and later on creates a rift valley.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
